
The Eastern Jin Dynasty map of Nanjing,by Chen Yi Stock Photo Alamy
In the south, an Eastern Jin Dynasty was set up by Sima Rui, a member of the Jin royal house. The Later Zhao was set up in 319 by Shi Le, a Jie tribesman and previously general in Liu Yuan's service, its capital being first at Xiangguo (southwest of present-day Xingtai City , Hebei ) and then at Ye (southwest of present-day Linzhang County.

Eastern jin dynasty hires stock photography and images Alamy
The Jin dynasty ( / dʒɪn /, [2] [tɕín]; Chinese: 金朝; pinyin: Jīn Cháo) or Jin Empire ( Chinese: 金國; pinyin: Jīn Guó; Jurchen: Anchun or Alchun [3] Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin ( Chinese: 大金; pinyin: Dà Jīn ), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234.
Jin Dynasty (11151234) Chinese History Ancient China Facts
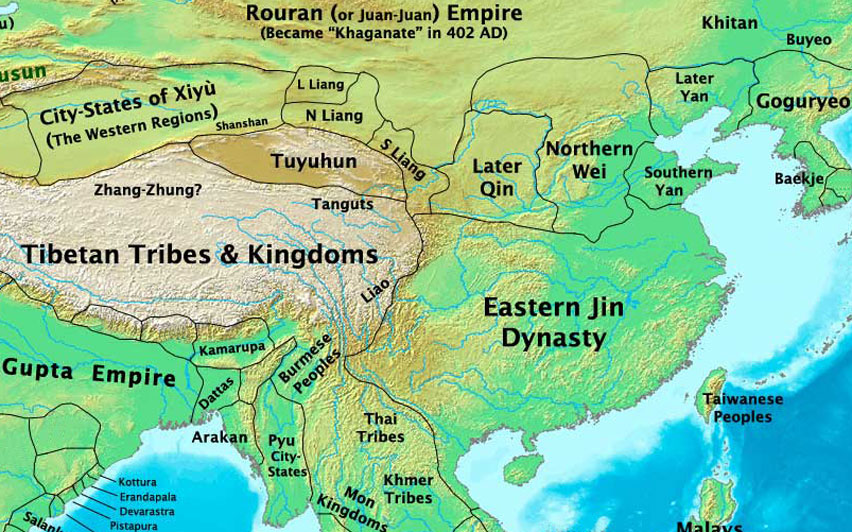
The Eastern Jin Dynasty (317-420) 东晋In a brutal rebellion known as the Wu Hu Uprising (304-316), the Jin Dynasty (265-420) was overrun by the northern tribal peoples and the north of China was lost. In 311, the imperial capital of Luoyang was captured and the reigning Emperor Huai was executed.

(382 CE) Administrative Divisions of the Eastern Jin Dynasty China
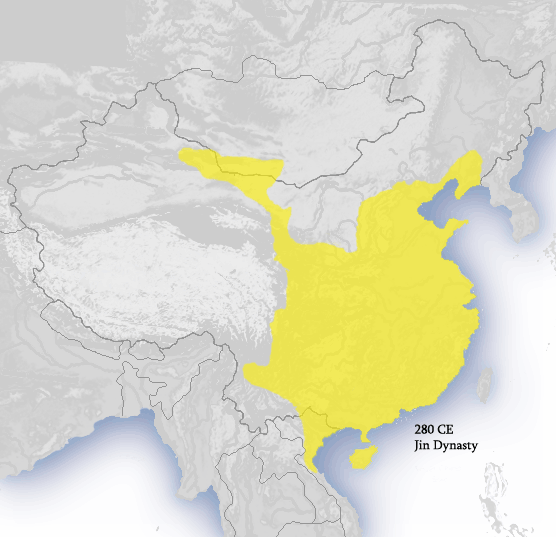
The Sima clan became the dynastic rulers of the Jin Empire (265-420). The dynasty lasted for 155 years, and for a while they controlled about the same territory as did the Han Empire. Beginnings of the Jin Kindom (220-265) In the year 220, the Han Empire divided into three kingdoms: Cao Wei (曹魏), Shu Han (蜀漢), and Dong Wu (東吳).

Pottery Ox Cart and Tomb Figurines, Eastern Jin DynastyNanjing Museum
The Eastern Jin Dynasty was established in 317AD and ended in 420AD. In the year prior to the establishment of Eastern Jin, the last monarch of Western Jin, Emperor Min had been captured by the Huns, and as a result, some former Western Jin ministers formulated plans to resume the dynasty in southern China.

ewer with chickenhead spout, Eastern Jin dynasty, Eastern Jin dynasty
Jin dynasty, Chinese dynasty that comprises two distinct phases—the Xi (Western) Jin, ruling China from ad 265 to 316/317, and the Dong (Eastern) Jin, which ruled China from ad 317 to 420. The Dong Jin is considered one of the Six Dynasties. In ad 265 a Sima prince, Sima Yan, deposed the last of the Cao emperors and established the Xi Jin dynasty.

Goatshaped celadon glazing vessel of Yue ware in Zhejiang Museum in
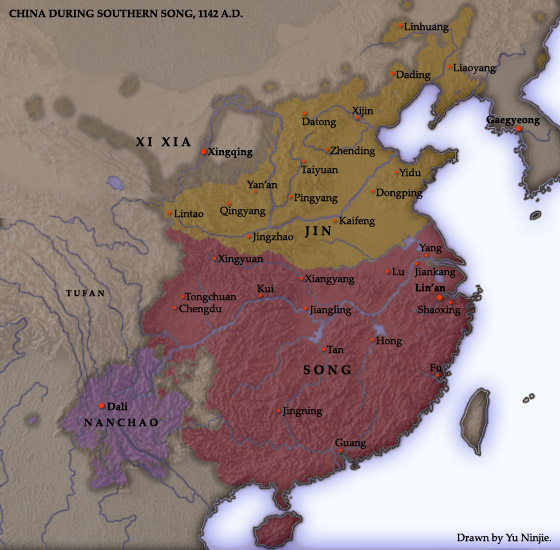
Restricted to southern China, the Eastern Jin Dynasty (317 - 420) was established by Sima Rui, a descendant of the royal family in the Western Jin Dynasty (265 AD - 316 AD). Eastern Jin governed for 103 years under 11 different emperors. It was so-named because it succeeded Western Jin and the capital city, Jiankang (Nanjing of Jiangsu.

PPT Jin Dynasty PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2724003
With the establishment of the Eastern Jin dynasty in southern China in 317, the transplanted throne was eager to gain the allegiance of powerful southern gentry families; thus, men such as Ge Hong were showered with official appointments, which were usually more honorary than substantive in nature. In recognition of his past military successes.
China, Eastern Jin Dynasty Map, 400 AD Nations Online Project
Eastern Jin Dynasty Set up in 317 and ended in 420, the Eastern Jin Dynasty was successively reined by 11 emperors. Established by the last of the Western Jin and governing a limited area lying to the South of Yangtze River, this dynasty was recorded as a single dynasty in Chinese history. Political History

Ornamental Plaque China Eastern Jin dynasty (317420) The
The War of the Eight Princes (291-306 CE) is the conflict which weakened and finally ended the Western Jin Dynasty (266-316 CE) in China and resulted in more far-reaching consequences throughout the country. The power of the Sima family was established in the State of Wei by Sima Yi (l. 179-251 CE) during the period of the Three Kingdoms prior to the rise of the Jin Dynasty.
Picture Information Map of Eastern Jin Dynasty
The literature in the Wei and Jin Dynasties started from the first year of the reign of Emperor Xian of the Eastern Han Dynasty under the title of Jian'an (196) to the second year of Emperor Gong of Eastern Jin Dynasty under the title of Yuanxi (420). During the Jian'an period in the late years of the Han Dynasty, "the Jian'an Literary.

The Jin Dynasty, China Jin Dynasty History, Chinese Jin Dynasty Facts
1 A.D. 125 A.D. Western Han dynasty, 206 B.C.-9 A.D. Wang Mang interregnum, 9-25 A.D. Eastern Han dynasty, 25-220 A.D. Overview The Han dynasty (206 B.C.-220 A.D.) establishes China's lasting model of imperial order and imposes a new national consciousness that survives today among the Chinese, who still refer to themselves as the "Han people."

265 420 Jin Dynasty
The section of the MWS that the Mongolian Arc belongs to has previously been associated with the Jin dynasty (A.D. 1115-1234) and is believed to have been built during this period. But this.
Jin Dynasty (265420 BC) Chinese History Ancient China Facts
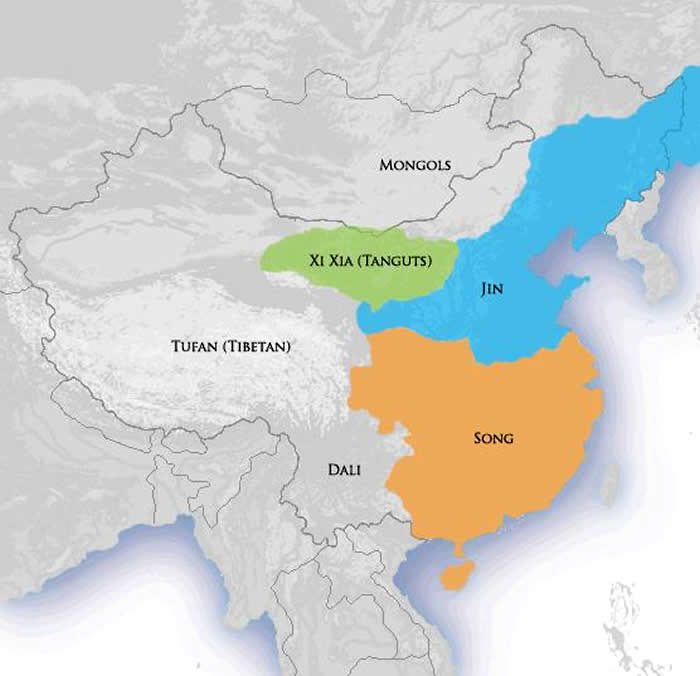
The Jin Dynasty consists of two dynasties, the Western Jin (265 -316) and the Eastern Jin (317 - 420). The Western Jin was founded by Sima Yan with Luoyang as its capital city while the Eastern Jin was founded by Sima Rui with Jiankang (currently Nanjing) as its capital. In 265, as a chancellor of the Kingdom of Wei, Sima Yan forced the last.

Pottery Ox Cart and Tomb Figurines, Eastern Jin DynastyNanjing Museum
Amid gathering indications of dynastic doom, in 306, Sima Yue (d. 311), the final victor in the vicious "Disturbances of the Eight Princes" ( bawang zhi luan ), that had been the immediate cause of much of this dynastic collapse, appointed his nephew Sima Rui (276-323) to a garrison command at Xiapei, near the modern city of Xuzhou, toward the s.

Jin Dynasty (265420), Eastern Jin (317420) in 400 Jin dynasty
Jin dynasty, or Chin dynasty, Period of Chinese history ( ad 265-420) following the Three Kingdoms (Sanguo) and preceding the Southern Dynasties (Nanchao) periods. It is the first of two major Chinese dynastic periods to bear that name, the other Jin (or Juchen) dynasty ruling in 1115-1234.