
Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimate and How to Calculate It (with
The rough order of magnitude is the cost calculation that could be used for multiple programs. The examples of works that fall under this category are policy formulation and execution, IT projects, and construction projects. Rough order of magnitude is most widely used during the planning and start-up stages of a project.
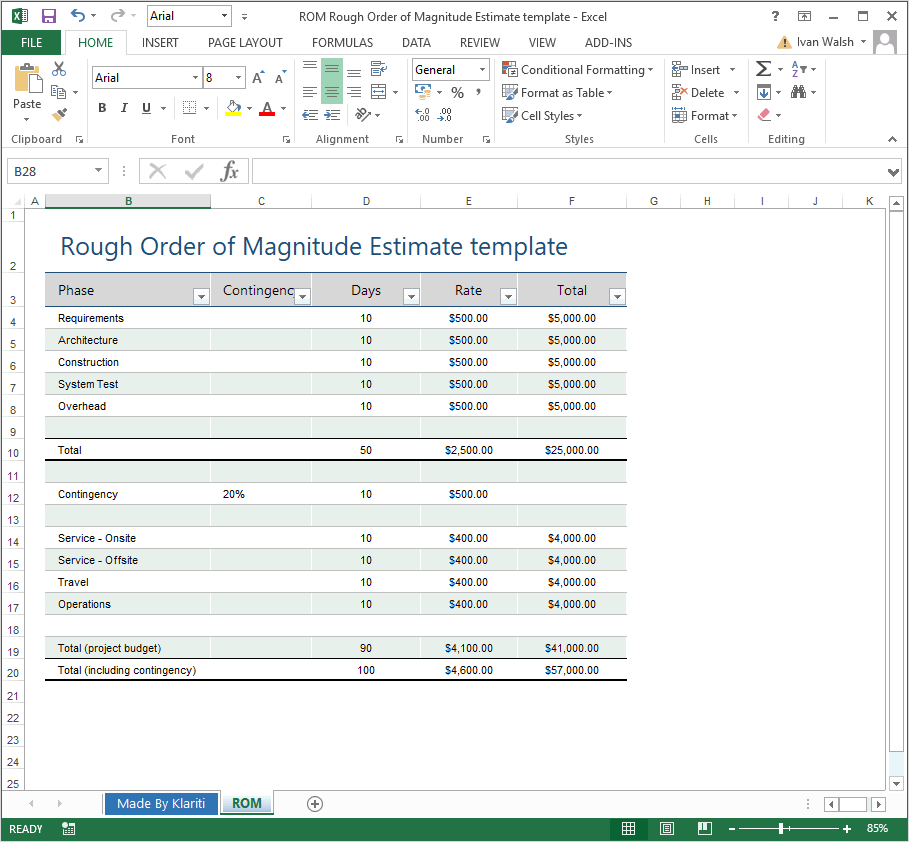
Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimate Excel template Templates
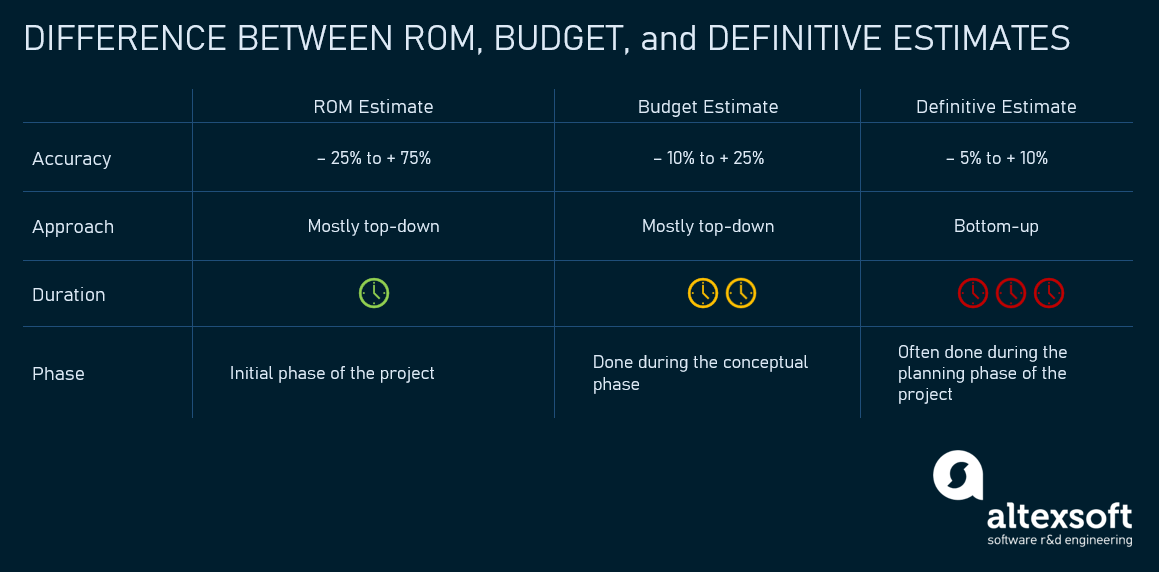
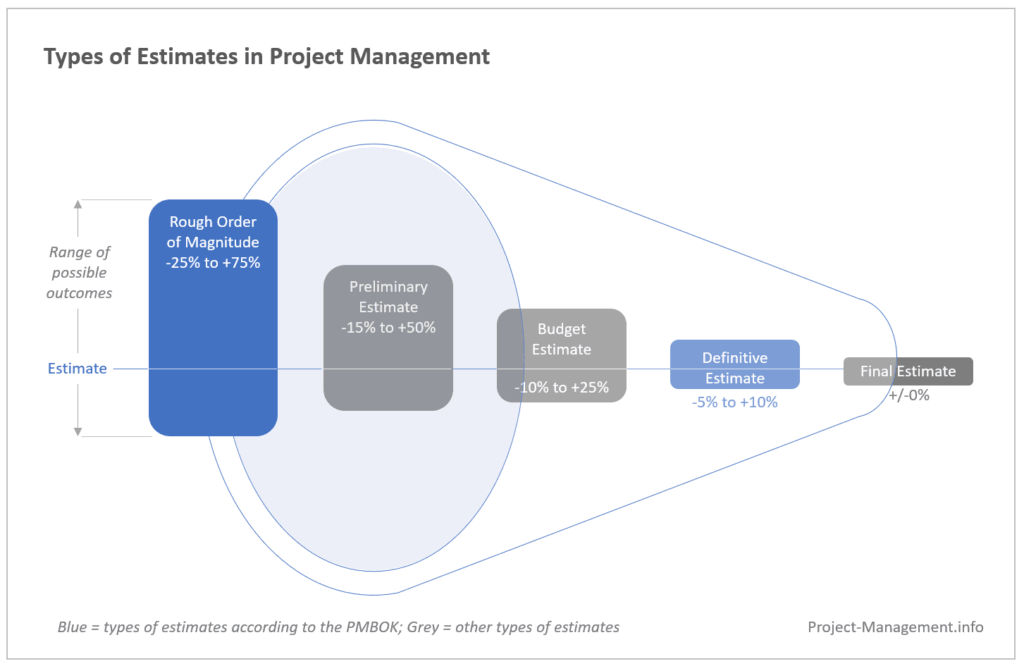
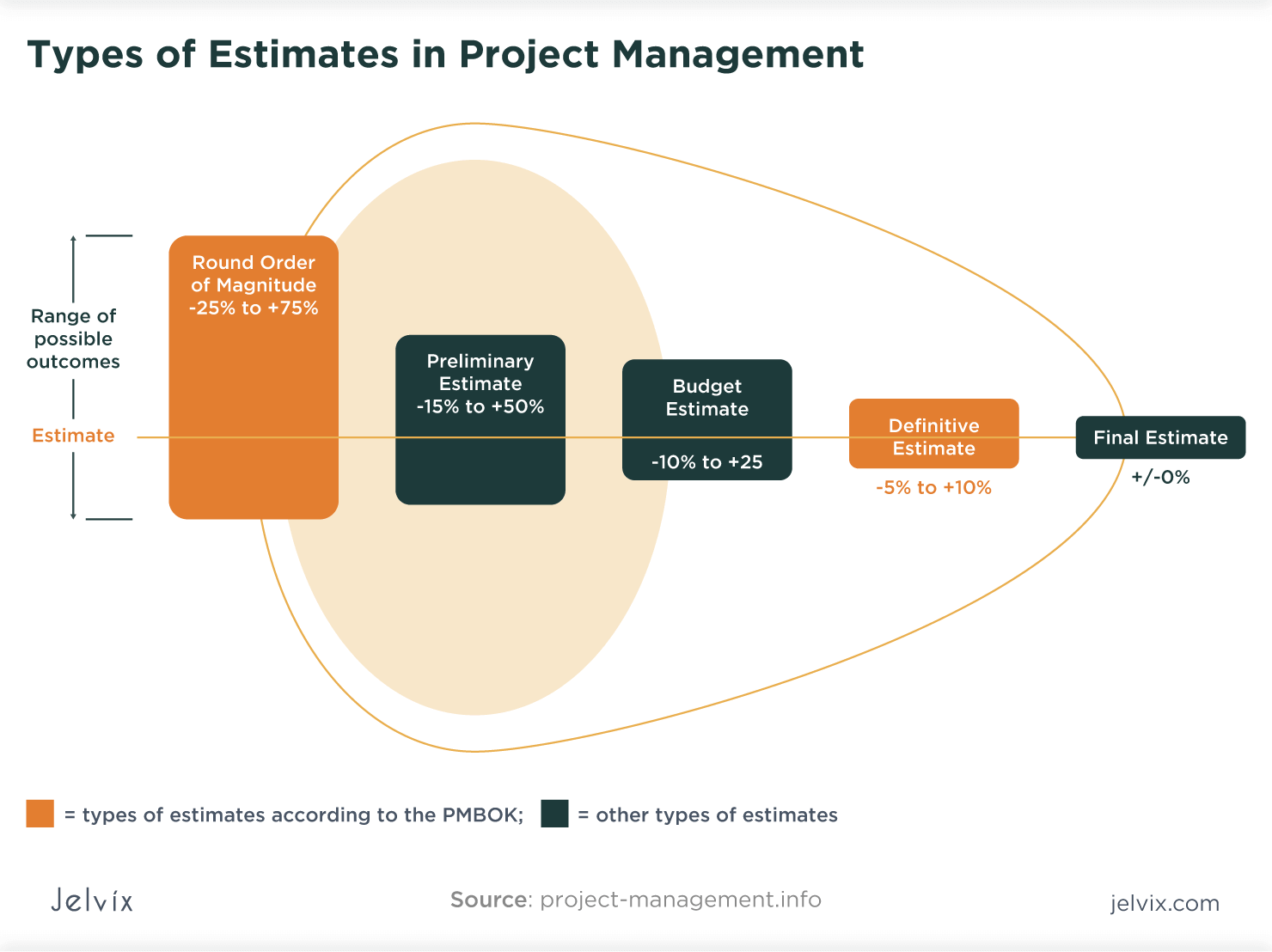
Definitive estimate and rough order of magnitude (ROM) are two classes of estimates that are defined in PMI's Project Management Body of Knowledge. They differ in their levels of accuracy. ROM normally has an accuracy range between -25% and +75%. For definitive estimates, it ranges from -5% to +10% (PMBOK®, 6th ed., ch. 7.2).

Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) vs. Definitive Estimates YouTube
A rough order of magnitude estimate is a general estimate of a project's level of effort and cost. It's usually performed during the selection and approval stage of a project. Generally, it's used for estimating a project budget that doesn't have a lot of detail.

Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Vs Definitive Estimate
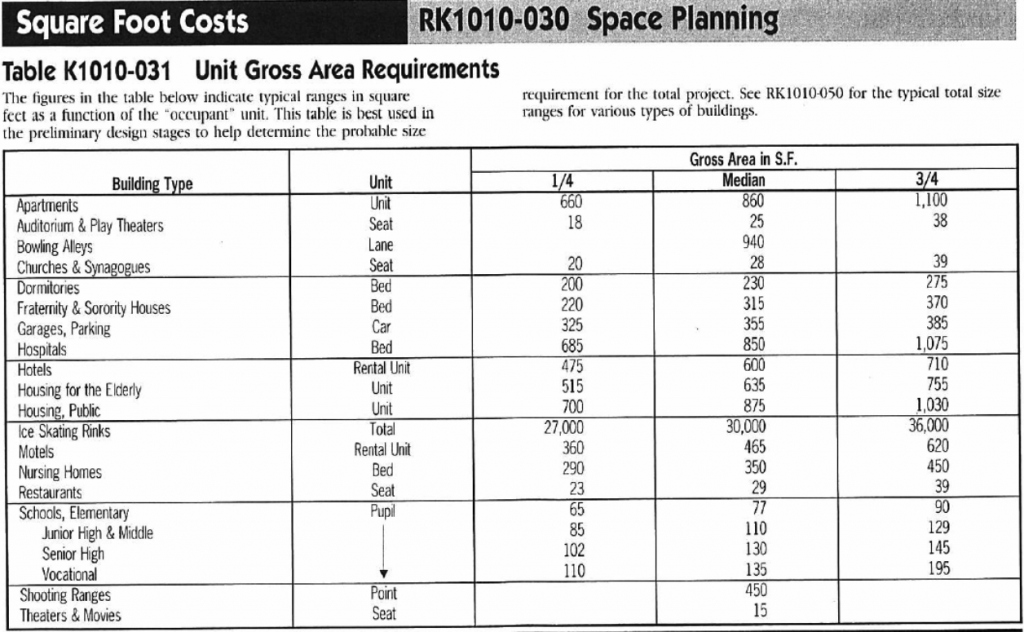
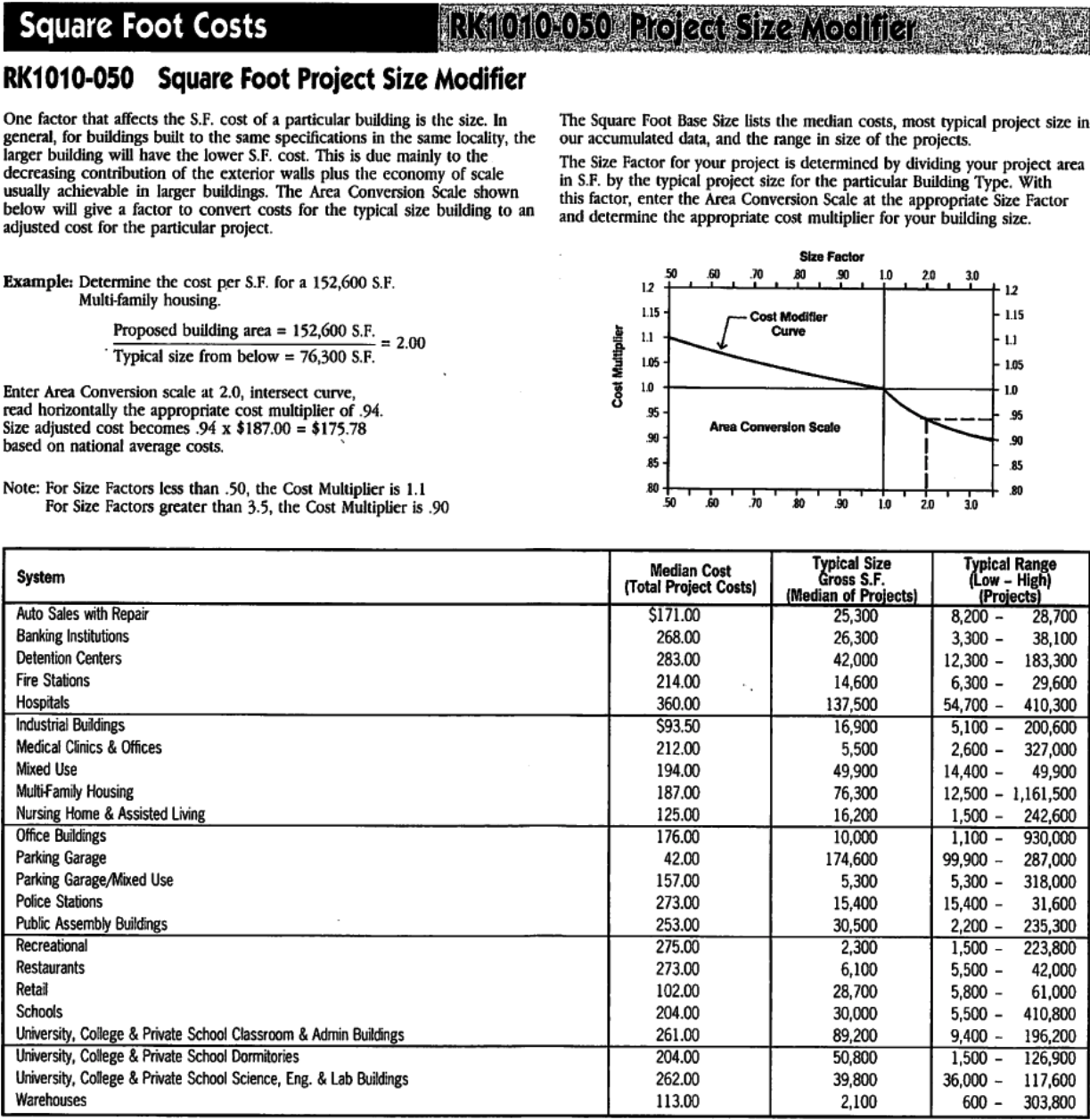
Figure 6-1: Description of the Rough Order of Magnitude Estimating Approach with RS Means Data To perform the estimate, you can either have an approximate footprint or size (square foot) for the building, or you may know the programmatic use of the facility along with a key use quantity, e.g., number of cars for a parking garage, number of beds.
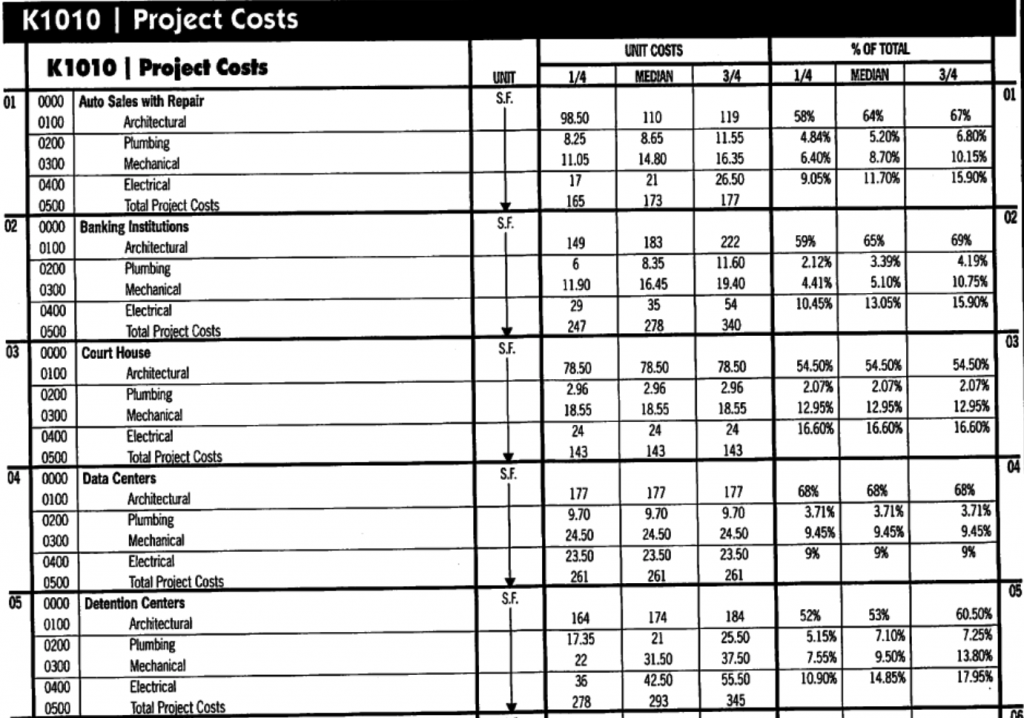
Chapter 6 Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Cost Estimating
Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Range Calculator Once you have entered your initial estimate, the calculator will automatically determine the minimum and maximum values of your ROM range. The calculation follows the PMBOK description, i.e. the lower boundary is 25% below the estimate and the upper limit is 75% higher than the initial estimate.
Rough Order of Magnitude How to Determine It and Pitfalls to Consider
A rough order of magnitude estimate is used to give you a very high level view of potential project costs. Ideally, you'd be able to provide a definitive estimate, carefully created from loads of input from subject matter experts and plenty of research on past projects and their budgets.
Rough Order of Magnitude Definition, Types, and Use Cases
Let's get started. What is the Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimate? A rough order of magnitude is a high-level estimate of the project. Management uses this technique to know the approximate budget requirement for the project during the feasibility study or project selection process.

Rough Order Of Magnitude Estimate Template DocTemplates
Rough order of Magnitude (ROM) Cost A ROM Cost is a general approximation of the cost of providing a stated service. It is based on experience, costs of similar services, or on a cursory examination of other vendor's rates. A ROM Cost is usually provided to a Customer who is seeking general information.

Free Rough Order of Magnitude Template (Google Sheets)
Rough Order of Magnitude Estimate. An estimate based on high-level objectives, provides a high-level view of the project deliverables, and has lots of wiggle room. Most ROM estimates have a range of variance from -25% all the way to +75%. No items have been linked to this term.
Definitive Estimate vs. ROM/Rough Order of Magnitude (+ Calculator
A Rough Order of Magnitude estimate, often called ROM Estimate, is the first estimate in the life cycle of a project. Usually it is used for project screening, that is, to decide which among several projects to proceed with. It is also often used to estimate projects prior to funding being approved. Accuracy
Chapter 6 Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Cost Estimating
This generic estimation of the scope and cost of a project is known as a rough order of magnitude estimate in project management. This estimation is done when a project is at the selection and approval stage or the pre-intake phase of the project.
Rough Order of Magnitude Definition, Types, and Use Cases
Rough order of magnitude (ROM) refers to an initial estimate of the cost of a project or parts of a project. It has an expected accuracy of -25% to +75% according to the PMBOK (other sources suggest -50% to +50%). In other words, the actual costs of a project are typically expected to be between 75% and 175% (or 50% to 150%) of the ROM estimate.

Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Types, Examples
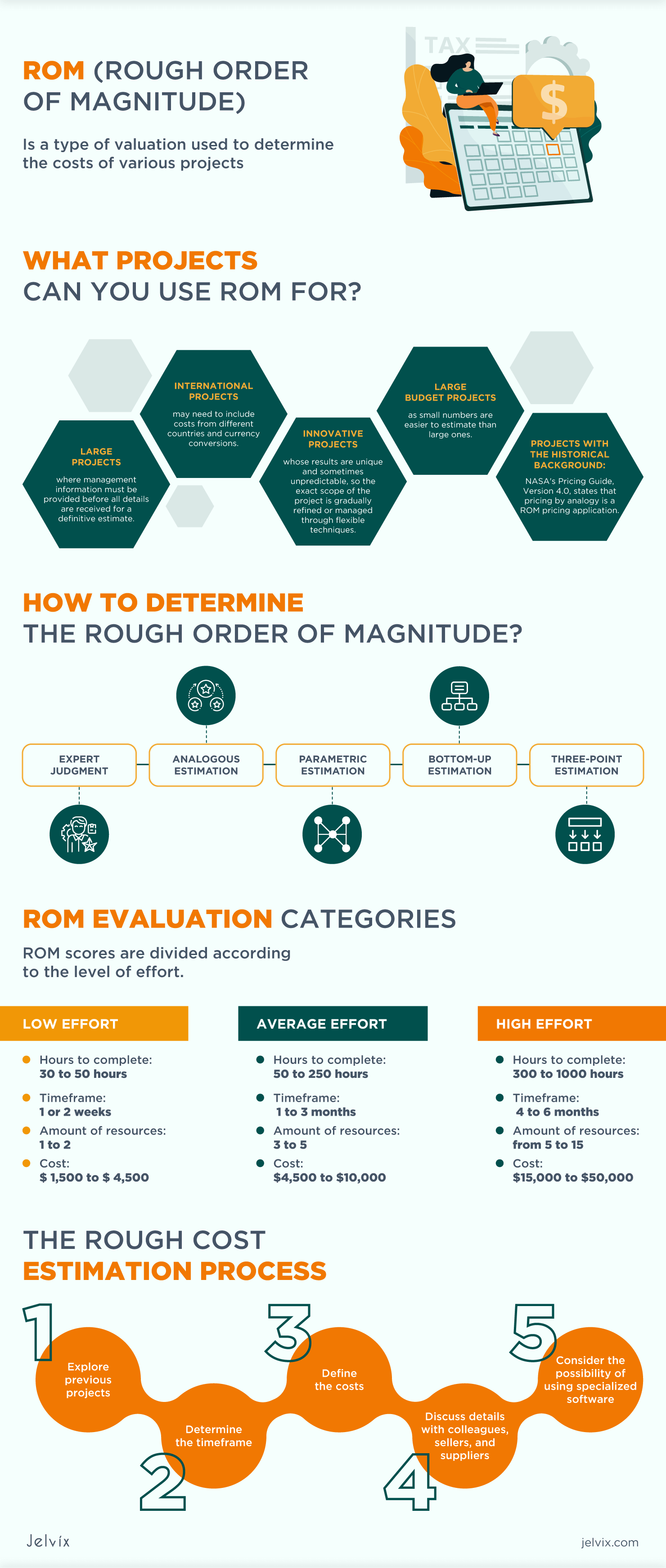
A rough order of magnitude (ROM) estimate is a preliminary, high-level estimation process. The goal here isn't to give a concrete answer of exactly how costly a given initiative might be, but to give just enough details to facilitate proper planning and decision-making. We use ROM estimates for:

What is a Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimate?
In project management, rough order of magnitude (ROM) is a rough estimate of the cost or size of a project. It is usually expressed as a single number that represents a range of values. ROM estimation is a relatively simple technique that can be used to quickly estimate the likely cost or duration of a project and it is often used in the early.
Chapter 6 Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Cost Estimating
A quick, broadly scoped cost estimate that is typically completed when few details exist on a specific effort. By creating ROM estimates, programs can develop general ranges for the cost of requirements. ROMs are utilized predominantly in the early stages of the acquisition lifecycle - or in the early stages of a contractor's interaction.
Rough Order of Magnitude Definition, Types, and Use Cases
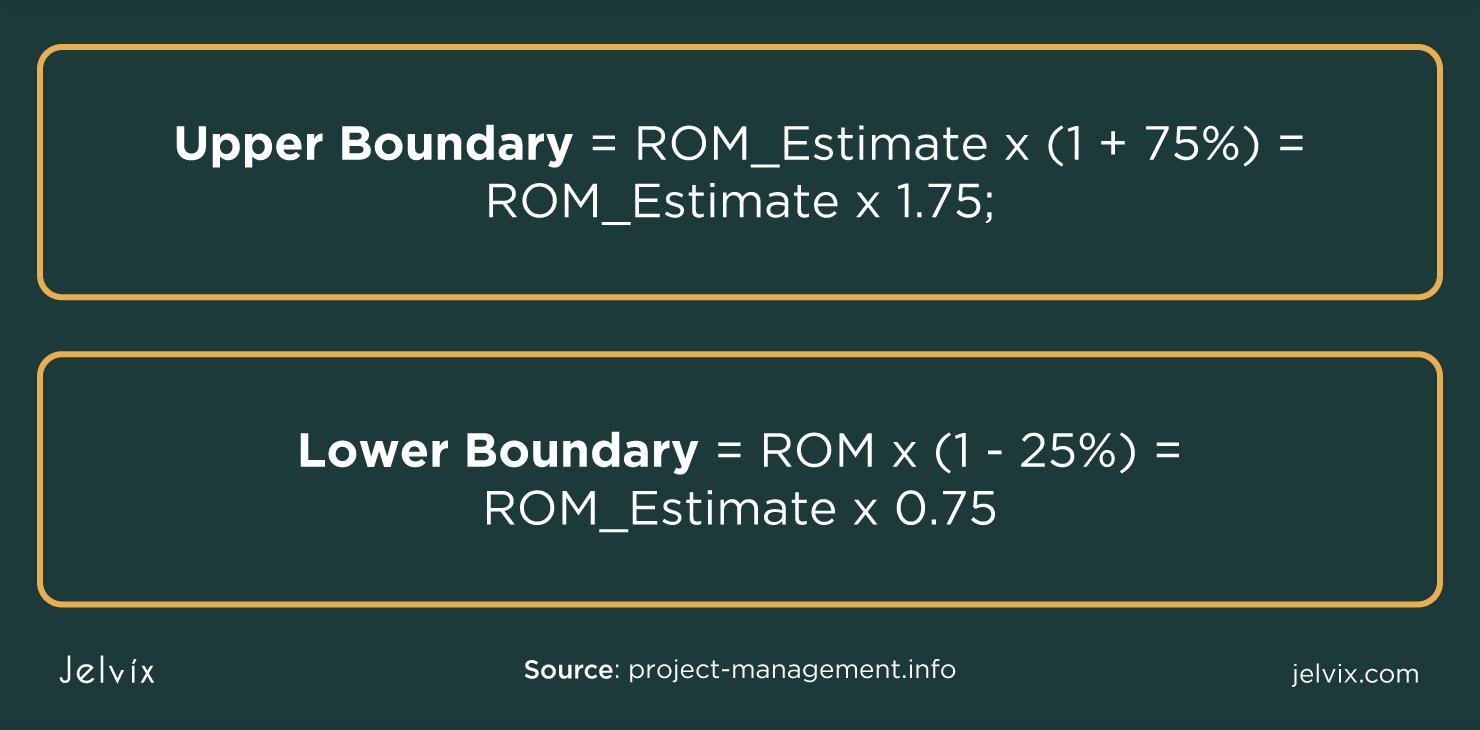
A rough order of magnitude estimate is a calculation that requires a formula. That formula is twofold to capture an upper boundary and lower boundary range. The formulas are below. Upper Boundary = ROM Estimate x (1 + 75 percent) = ROM Estimate x 1.75 Lower Boundary = ROM Estimate x (1 - 25 percent) = ROM Estimate x 0.75